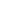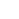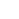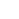LOT 39 STATUE D'UN BODHISATTVA EN SCHISTE GRIS ANICENNE RÉGION ...
Viewed 159 Frequency
Pre-bid 0 Frequency
 Collect
Collect
Name
Size
Description
Translation provided by Youdao
STATUE D'UN BODHISATTVA EN SCHISTE GRISANICENNE RÉGION DE GANDHARA, VERS IIIE SIÈCLE115 cm (45 1/4 in.) highProvenance: A GREY SCHIST FIGURE OF A BODHISATTVA ANCIENT REGION OF GANDHARA, CIRCA 3RD CENTURY犍陀羅 約三世紀 片岩菩薩像Published:Isao Kurita, Gandharan Art, Vol. II, Tokyo, 1998 & 2003, p. 15, no. 17.Provenance:With Claude de Marteau, Brussels, by 1970sThis majestic figure of a standing bodhisattva evokes both strength and grace. He bears the qualities of a youthful prince, indicated by his jewelry and noble, smooth physiognomy. His pronounced musculature, circular nimbus, and lofty expression convey an idealized image of a divine and enlightened being. He likely represents Maitreya, who in Mahayana Buddhism is destined to succeed Shakyamuni as the next and final Buddha. Maitreya in Gandharan art is frequently depicted with a loosely folded topknot, a right hand raised in the gesture of reassurance (abhaya mudra), and a water flask that was presumably clutched by the lost lowered left hand. Reflecting the cosmopolitan attitude of Gandharan art, which fused Indic content with Iranian and Greco-Roman aesthetics, Maitreya is carved with long wavy locks, standing with a gentle contrapposto in the right knee. Located in what is today northwest Pakistan and southern Afghanistan, the ancient region of Gandhara was once a vibrant economic and cultural hub with an integral position within both overland and maritime silk routes around the 1st century BCE. The vast influx of wealth andmerce enabled Gandhara's urban centers to serve as the crossroads connecting China, Central Asia, the Indian peninsula, and the Mediterranean. However, Gandhara's advantageous geography meant the region fell repeatedly to invasion from powerful ancient empires. Alexander the Great conquered the ancient capital of Taxila in 326 BCE and the region was, for a brief time, absorbed into the Macedonian empire. After the death of Alexander, the Mauryans subsequently ruled for approximately one hundred and fifty years (c. 305-180 BCE). Greco-Bactrian invasions around 180 BCE then turned the region into an independent Indo-Greek kingdom (c. 185-97 BCE). One of its most famous rulers, King Menander I (r. 165/55-130 BCE), became a great patron of Buddhism and is still remembered for his dialogues with the Buddhist sage Nagasena, as recorded in the Milinda Panha, 'The Questions of Menander'. The Kushans, who were originally of Central Asian descent and adopted Greek and Iranian elements in their material culture, later established themselves in Gandhara in the early 1st century CE. The most aplished of these kings was Kanishka I (r. 127-151 CE), who not only ruled a vast empire extending from Bactria to Pataliputra in Northeast India, but also followed the tradition of religious patronage set by the Indo-Greek kings and actively engaged in the creation and transmission of Buddhist literature, architecture, and art. It was during this cultural landscape o
Preview:
Address:
Paris, France
Start time:

Online payment is available,
You will be qualified after paid the deposit!

Online payment is available for this session.

Bidding for buyers is available,
please call us for further information. Our hot line is400-010-3636 !

This session is a live auction,
available for online bidding and reserved bidding